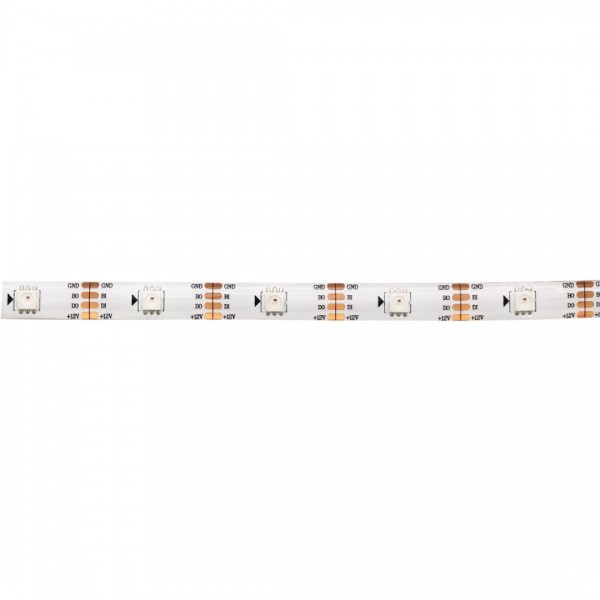
WorldSemi WS2815B Digital 5050 RGB LED Strip - IP65 - White - 150 LEDs 5m
- Availability: Directly available from warehouse in Eindhoven
- SKU: 005029
€32.00
Ex Tax: €26.45
10 or more €31.00
20 or more €30.00
50 or more €29.00
100 or more €28.00